Arrhythmia
funny sodium channels
depolarisation of excitation conduction cells
normal path is
- SA
- atria
- Av node
- Bundles of his
- ventricles
pattern can be changed by:
- IHD
- hormones
- drugs
- anatomical anatomy
Arrhythmia can be Atrial Fibrillation/SuperVentricular Tach or Ventricular Tachycardia/Ventricular Fib
arrhythmias can cause sudden death and also can be asymptomatic
usually caused from impulse generation brady tachy cardia
or impulse propagation dropped beats or heart block
Impulse generation defects
a. enhanced/altered automaticity
other tissue begin to outpace the SA node due to increase Na+ permeability
latent pacemaker cells produce ectopic beats
b. mechanisms of triggered activity (normal ap triggers extra abnormal depolarisation)
early after polarisations (torsades so pointes)
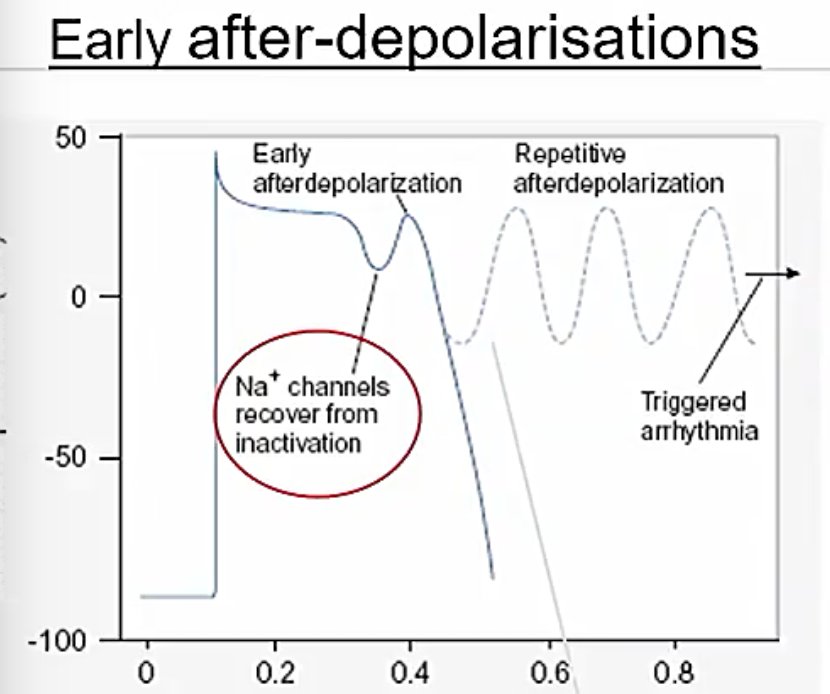
delayed afterpolarisations
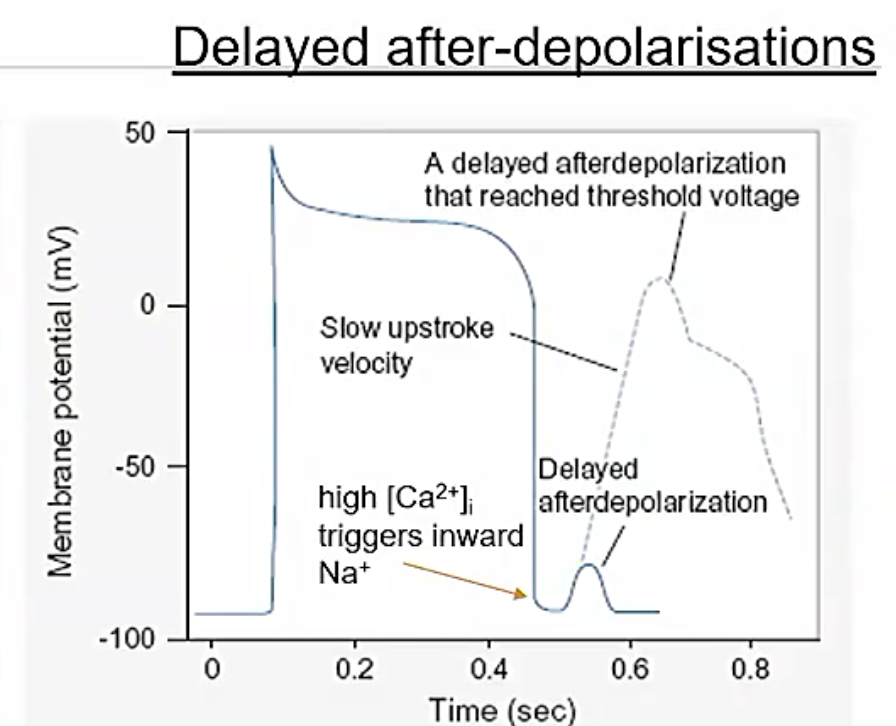
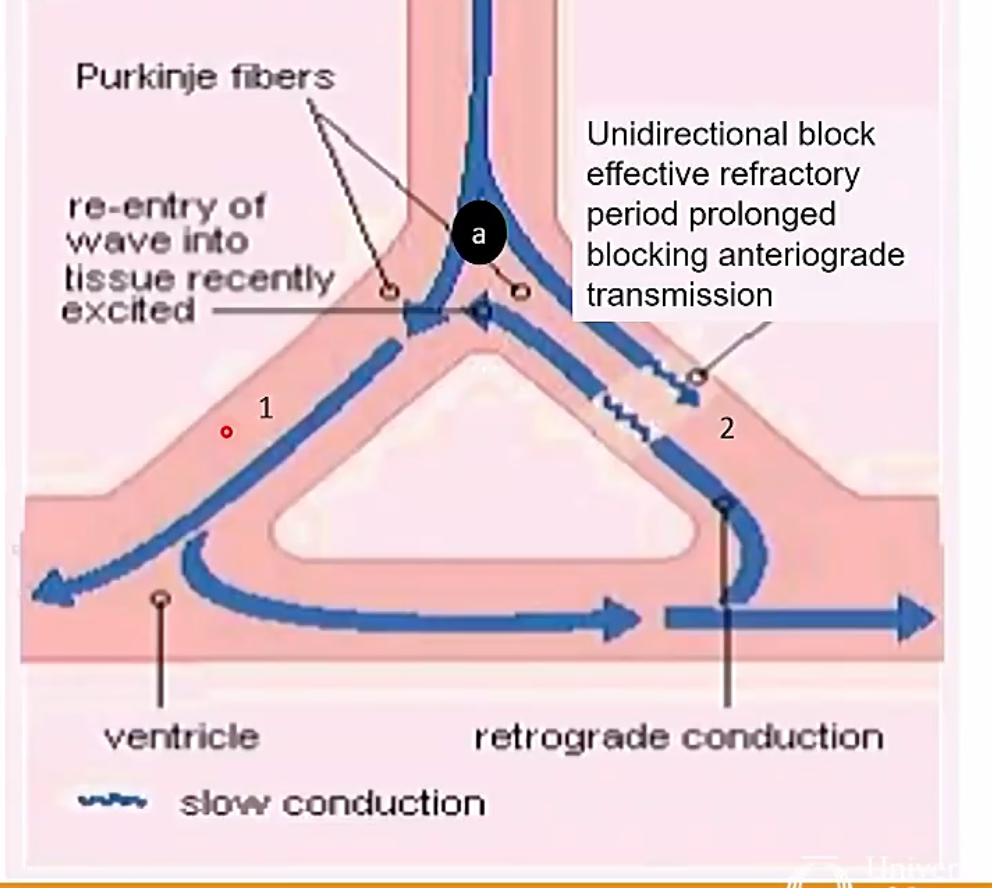
impulse conduction defects
HEarty block reentry accessory tract when the impulse doesnt wait for atria to contract to AV node
stress cardiomyopathy
Unidirectional block
cal lead to generation cells
Atrial fibrillation
causes: many
classification paroxysmal (self terminating) persistent (sinus responsive to treatment) successful AF ablation (free from AF) permenant (sinus cannot be maintained early rhythm control needed)
Treatment of AF
- treatment of rate/rhythm (lecture subject) (rhythm harder to treat)
- prevention of embolic complications (ischaemic stroke or pul embol)
AF treatment
rate control
Pharmacological
Bblockers ca2+ digoxin amiodarone
non pharmacol
ablate and pace
SR maintainance
pharmacol
class Ia class iB class III b blockers amiodarone
nonpharmacol
ablate pace surgery implant
stroke prevention
DOACs dabigatran
VKAs warfarin
Title
in patients with valvular disease or replacement warfarin is needed
Pacing and ablation vs pharmacological strategies
used when pharmacolgocial intervention fails or because adverse effects
Antiarrhythmic drug classes: (Vaughan Williams Classification)
these work for suppressing cardiac arrhythmias via inhibiting automaticity, triggered activity and reentry
generally works better with abnormal tissue with high heart rate
success is variable depending on condition
overdosing can promote arrythmias small difference between TI and toxicity
Mortality
- Class 1 can cause many probloems
- class 2 can descrease HR lead to poor lifestyle
- class 3 after 5 yr 75% of patients have ADRs (gi and vision)
- class 4 similar to 2
Class I - Na+ channel blockers (lignocaine)
- Reduce phase 0 slope and peak of AP 3 sub classes
block Na+ channel and slowes conduction velocity
lignocaine binds to NA mostly in open and inactivated states
indications
lignocaine polymorphic VT flecainide for chemical cardioversion
Unwanted effects arrhtymias
Class II - B blockers (metoprolol)
Block sympathetic action so slows at the SA node and increase pause in AV node
Indications first line for arr rate control may prevent reentrant tachy at av site use in SVTs and possiblt VT precipitated by exercise decrease mortality postMI
ADRs from exaggerated doses Severe AV node block fatigue uncompensated HF metoprolol can traverse bbb
Contra avoid in AV block avoid in sinus node dysfunction avoid in any eide comples tach
abrupt withdrawal can lead to rebound worsening angina mi ventricular arrhythmia higher bp makes malaise sweating etc
let off gradually but in bradycardia just need to stop dosages
Class III - K+ channel blockers (Amiodarone)
“Dirty drug” prolongs heartbeat by impacting on repolarisation prolonging plateau and AP duration but just changes a whole bunch prolongs ERP decreases chance of reentry block
prolongs artial and centricualr repolarisation if you overprolong you can get tdp
Uses: rate control effects on warfarin and digoxin joint use on b blocker can result in heart block use after resus after adrenaline release or shcok
ADRs multitude of ADRs rarely associated with proarrhythmic action though features that may complicate use gradually oral loading long elimination half life damages vein undiluted
Class IV Ca2+ channel blockers (Diltiazem)
same as CCB lecture lass inotropic and chronotropic actions
Use ratec ontrol in AF avoid combines use with b blockers
Miscellanous (Digoxin, atrophine, adenosine)
Derived from foxglove
Digoxin increases force of contraction (Cardiac glycoside) MOA1: blocks nak atpase
higher na in cell
indirectly inhibits nain caout
more calcium in heart
slows hr (vagal effect) Moa 2: also increases ACh release not fully understood
digoxin induced ACh release onto M2 recpeotrs reduced sa firing reduced Av conduction velocity
Digoxin is a dangourous drug
Diuretic should cautiously be used with digoxin due to hypokaleamia leading to more issues
dyr