Objectives
Understand:
- Psychological treatment for mental disorders and CBT in particular For examination:
- Be able to give a brief definition of what CBT is
- Demonstrate an understanding of the 4 core CBT techniques by applying a technique to a case
Treatment aptions
Psychotherapy
This is generally base therapy
Pharmocotherapy
This is generally for more severe cases
Really personalised medicine is important
What is psychotherapy
This is talk therapy, treatment of a mental disorder by psychological means.
There are a lot of forms of psycho therapy, one that we look at is CBT. WE do CBT because it is really common
Psychotherapy can be individual, couple, gorup or more
CBT
Very common and good for
- Anxiety
- depressive
- eating disorders
- Alcohol and drug disorders Ans you need to know what it is
What is CBT
short term psychological treatment that focuses on links between people thoughts, emotions and behaviours
Its regearing thoughts to better emotions and therefore helping behaviours. if you think more optimistic thought sometimes things just get better (cliche i know)
CBT is usually:
- time limited
- highly structured
- assessment and goal driven
- targets key area which propagate problem.
- cycles of though behaviour and feeling that ultimately feed back into problemor make it worse
Example of maintaining cycle
- fear of disaster (sky falling)
- Safety behaviour (15 jumping jacks)
- Failure to disconfirm threat (no sky falling bc i did jumping jacks)
How do we do it?
Firstly we make connections between thoughts and feelings. “When you think X you tend to feel Y”
Core techniques 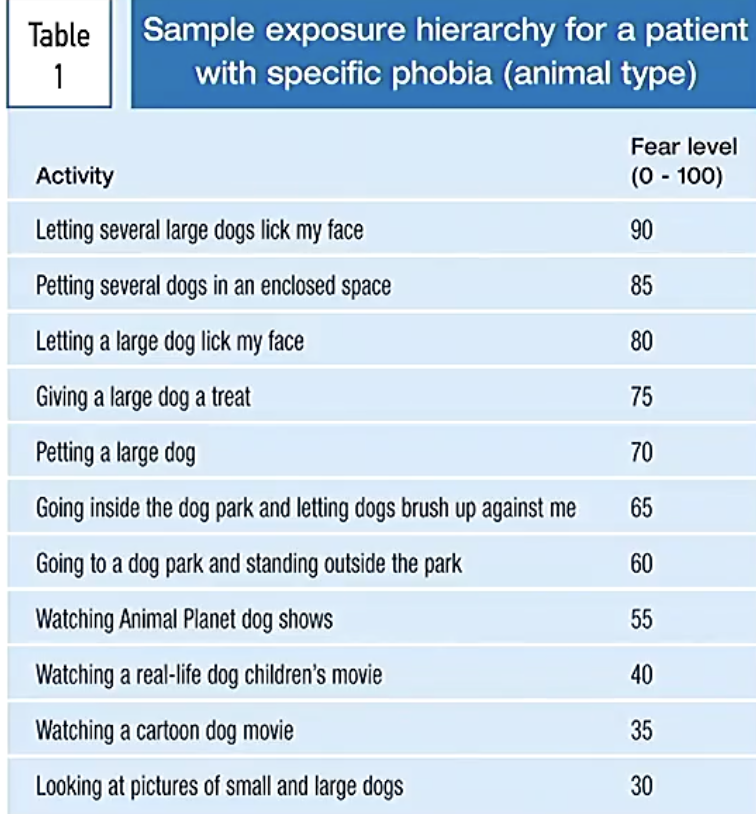
1. Graded exposure
We directly target the avoidance that causes fear. This results in challenging the association between thing and threat. Additionally over time anxiety goes down in a situation when you get used to it.
Specifically what it is we get the patient to rate level exposure to a thing on a scale of 0 (easy) - 100 (unbearably hard) and develop a hierarchy of steps of exposure.
Choose the steps collaboratively
Also learning anxiety is not dangerous Also doing homework Also approaching cognitions.
2. Exposure and Response prevention
This is being exposed to think and deliberately stopping the response prevention.
This is often session plus homework
3. Behavioural experiments
This is experiments to test unhelpful beliefs or predictions in reality.
For example “if I stay in a public place I will collapse” get them to do into the thing as see results
Grading is important: Have client rate how sure they are of something happening. They can then test it themselves or see someone else testing theory. then have them regrade.
4. Evidence for and against
Identify unhelpful beliefs.
Get them to write it down and evidence for, and then evidence against.
than get them to recollect on the thing on the whole