Adrenergic Modulators a.k.a Beta Blockers

Background
factors controlling BP
MABP = CO + TPR.
To decrease MABP you can decrease CO or TPR. (OR volume)
This can be done by Blocking or reducing sympathetic action.
Also baroreceptor reflex:
- baroreceptors detect low BP and trigger adrenaline release to adrenergic receptors (sympathetic) to get Bp up
Adrenergic receptors
Adrenergic modulators alter functionality at different adrengeric receptors, and depending on what they do different results result. Noradrenaline is a common Neurotransmitter so there are many different systems which can be targeted. Basically specifically lowers parts of the Sympathetic system. This can lower blood pressure along with other things
Drugs
Treatment guidelines for HTN
aceinhibitors/ arbs genetrally first line interventions Calcium channel blockers diuretic b blockers not seen as 1st choice for Isolated Systolic Hypertension control
Classifications
alpha 1 blockers (-zosin)
- doxazosin (often used with other drugs)
alpha 2 blockers
- clonidine
- a-methyldopa
Beta blockers (b1 for cardio selectivity) -olol
- metaprolol
- atenolol
- propranolol
- carvediol
This is the effect of each of the cardiorenal adrenoreceptors. Blocking each type should have the opposite effect
| a1 | a2 | b1 | b2 | b3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vascular SM | constrict | constrict | dilate muscle | ||
| Heart chronotrophy | +++ | + | |||
| Inotrophy | ++ | +++ | + | ||
| kidney renin secretion (up renin = up BP) | +++ | ||||
| nerves (reduce NA release preganglionically) | ++ | ||||
Lecture B: examples of drugs
Doxazosin (2nd to 3rd line treatment of HTN)
selective vascular a1 blocker reduce BP in mild to moderate HTN but not usually suitable as monotherapy
vasodilator: a1-mediated sympathetic tone relaxes smooth muyscel of both resistance vessels and veins
- reduced peripheral vascular resistance and increases venous capacitance
value; less reflex tachycardia then nonselective a blockers celectivity at a1 meands less likely to block a1 uretheric hyperplasia and benign prostatic hyperplasia good LDL/HDL profile
side effects
postural hypotension depression drowsiness nasal stuffines diarrhoea less ejac urinary incontenenct
a2 inhibitors
blocks presynaptic actions increase parasympathetic clonidine and a methyldopa effect posterior hypothalamys and medulla
less sympathetic firing
a-methyldopa is used in eclmapsia for pregnancy
Central action of a2 agonists
stops the reuptake of noradrenaline
initially raises bp due to vascular binding
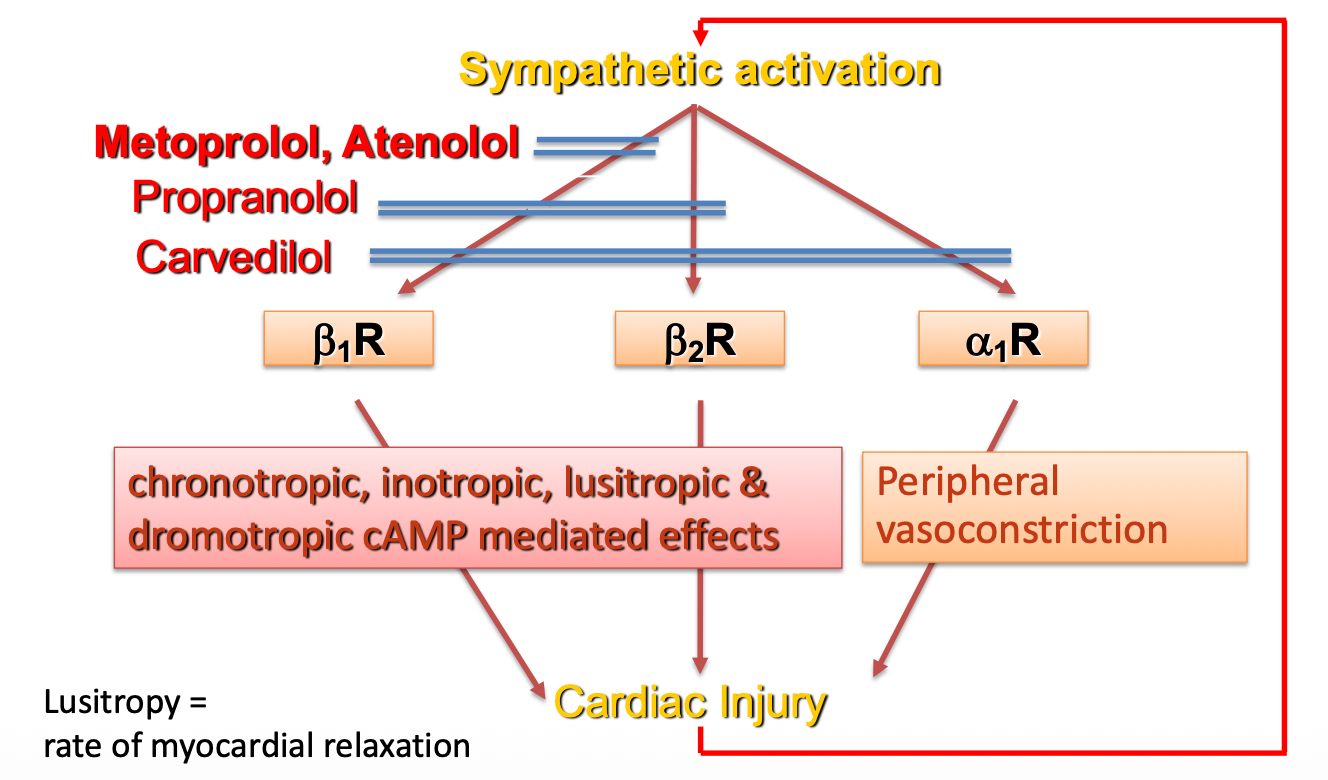
Beta blockers
metoprolol propranolol are inverse agonists, not only block receptor activation but decrease baseline effects
1st gen (propranolol)
2nd gen (Metoprolol)
3rd gen (Carvedilol)
Theraputic uses of Beta-blockers (Use cases)
cardiac rate control: antiarrhythmix used in atrial fibrillation angina and MI: makes hearts job easier Heart failure: use of carvedilol as vasodilating sympatholytic Hypertension (not generally used) used in conditions where SNS is overacting (most HTN patients suffer from atherosclerosis) Sometimes: Glaucoma: timolol in eye drops for decreases intraocular pressure Anxiety: for tremors and increased HR
Why aren't Beta-blockers used in HTN
1st and 2nd gen beta blockers reduce BP through -ve chronotropic and inotropic effects without vasodilation (while still negatively effecting lipid profiles)
3rd gen ß-blockers also have vasodilator capabilities without major adverse effects
Adverse drug responses of Beta-Blockers
-
bronchospasm due to b2 interaction
-
decreases CO can promote heart failure
-
Reduced exercise tolerance
-
peripheral vasoconstriction
-
worsening heart block
-
CNS effects (nightmares)
-
Worse lipid profiles
- inhibit b2 stimulation of vascular lipoprotein lipase
- increase vldl to HDL levels
-
also blunt catecholamine induced glycogenolysis in response to hypoglycaemia
3rd gen also vasodilates o more helpful and have less effects on HR lipid etc
atenolol hydrophilicity lack of hepatic first pass longer half life low CNS penetration
metoprolol and carvedilol lipophilic improved oral absportion hepatic metabolisn greater first pass howerer half life larger vol of dist resulting in ADR higher cns penetration
lipophilic drugs often vary in half life due to polymorphismns is cyp2d6
administration oral admin:metoprolol, c arvedilol, atenolol, propranolol. Taken with food to slow down absorption tartarate immediate release succinate extended release
rapid admin (IV) esmolol, labetalol. emergency and short acting
titrate dose up gradually withdraw slowly to avoid rebound effects
Pharmacodynamics
snp in ADRb1 gene leads to gly → arg and leads to increases inherent receptor sensitivbity to b blockers
also ser to gly results in smaller amount of b receptors and loss of response to b blockers
genetic variations in gene encoding CYp2d6 lbroad spectrum
ultrarapid response and low response