Corticosteroids (antiinflammatories)
Objectives
- what and where
- site mechanism and route of deliver using main examples of
- inhales corticosteroids
- oral corticosteroids
- site mechanism and route of deliver using main examples of
- when?
- Understand when anti inflammatory medications hsould be used int he management of umbrella conditions such as asthma and COPD
- adverse consequences and mitigation
- understand the liumitations and main adverse effects associated with each drug class. Show an understanding of devices and techniques to mitigate adrs
Definitions
Asthma COPD Asthma and COPD overlap
Arachadonic acid derivatives produced from mast call membranes
Pharmacological intervention preventers
Anti inflammatory compounds corticosteroids (glucocorticoids)
- inhaled
- fluticasone
- budesonide
- beclomethasone
- oral
- prednisone
Both glucocorticoids (cortisol) and mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone) are corticosteroids
Glucocorticoids
upregulate phospholipase inhibitor lipoocortin-1 which upregulated antiinflammatory and down regulates proinflammatory
- Fluicasone
- Budesonide
- Beclomethasone
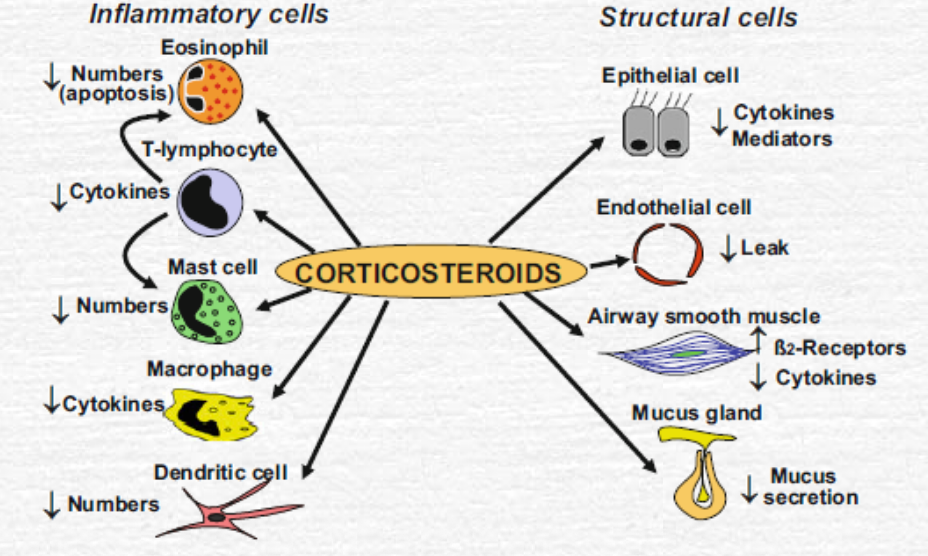
Relevant effects in astham
reduce recruitment inhibit macrophage function reduce vascular permability no effect on broncodilation but over time may decrease airways hyperresponsiveness
high dose oral steroids have lots of systemic ADRs including negative feedback of HPA. Will cause adrenal supression
Oral Corticosteroid usage has cushingoid side effects Glucocorticoid ADRS:
- list them
- systemic toxicity
- adrenal crisis
- assessment of future risk
Prevention of ADRs
Inhalation route minimises ADRS
Corticosteroids
Salbutamol