Objectives
- review cholesterol synthesis and transport
- Understand the significance of lipid profiles in cardiovascular pathologies
- develop an understanding of the key theraputic intervention targets and goals in managing hyperlipidaemias
Dyslipidaemia
Background
Lipoprotein lecture
- high association between dyslipidaemia and CV disease particularly in diabetes
- hence hypercholesterolemia treated as a major modifiable factor in the development of CHD, HTN etc
- dyslipidaemia con contribute to progression of vascular endothelial lesions, leading to thrombotic occlusion stroke MI renal injury etc
- Cv disease and kidney disease form a vicious circle fuelled by numerous known risk factos for CVD in patient siwth CKD, including oxidative stress inflammation dyslipidemia endothelial function vascular calcification insulin resistance and renal dysfunction
we can make cholesterol endogenously from acetyl-CoA. We can target this pathway
Cholesterol transport
HDL - picks up cholesterol - carries 20-30 percent of TAGs LDL - Most atherogenic carries 70-80% of TAGs IDL VLDL- not involved in atherosclerosis but precursor to IDL and LDL Chylomicrons transports FA and cholesterol from diet
We make cholesterol from Acetyl-CoA and HMG CoA reductase is a part of this
Lipoprotein motif types
ApoB lipoproteins VLDL IDL LDL Chylomicrons ApoA-I is HDL
Apoprotein B100 facilitates endocytosis of the LDL
Cholesterol cycle
The apolipoprotein facilitates endocytosis of the entire lipoprotein. question this needs to be resolved as my previous understanding was that vascular LPL cleaves tags into FFAs where the FFAs then diffuse into the tissues. i did not think the lipoproteins were endocytosed. maybe both are true
Raised intracellular cholesterol has 3 regulatory effects
- decreases activity of HMG CoA reductase
- activates ACAt to esterift free cholesterol into cholesteryl ester what can be stored in the cell
- inhibits the transcription of the gene encoding the ldl receptor s and thereby decreases the further uptake of cholesterol into the cell
PCSK9
BInds to ApoB and just breaks everything down including receptor
Cholesterol and Atherosclerosis
L15 CVS Lipoproteins (as risk factors for heart disease) Atherosclerosis is highly associated with high cholesterol
Reported mechanism is ldl infiltrates endothelium and this triggers macrophages (oxidised Cholesterol causes this i think) to endocytose and turn into foam cells which along with growth factors and metalloproteinases cause cell proliferation and matrix degradation.
Atherosclerosis associated with
inablility to sequester and export cholesterol caused by
- High cholesterol diet
- deficiency in LDL apo B receptors
Atherosclerosis is
- Low LDL-ApoB receport numbers
- leads to reduced rate of lDL clearance
- Cholesterol is trapped in the bloodstream
- cholesterol deposition in tunica intima
Drugs For dyslipidaemia
Objectives
To deliver the principle theraputic MOAs with relevance to clinical cases to describe the cardiovascular effects use and adverse effects of these drugs Study the following drug class and specific example Statins: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (atorvastatin)
cholesterol uptake inhibitors: ezetimibe PCSK9 monocloncal inhibitors: evolocumab Bile acid binding agents
Antihyperlipidaemics
- Endogenous Cholesterol Ester attenuators
- Statins
- PCDJ9 inhibitors (used when you have reached max doseage on statins)
- Fibrates
- Exogenous CE attenuators
- Cholesterol reuptake inhibitors
- Bile acid binding resins
Statins
These inhibit HMG-CoA Reductase Most effective treatment for dyslipidaemia used for high LDL to HDL or TG to HDL ratios
Mechanism of action
reversible competitive HMGCoA inhibitors mainly decrease hepatic de novo synthesis of cholesterol causes increases LDL receptor synthesis as a result
- more LDL clearance lower plasma LDLs - cholesterol
- slight increase in plasma HDL - cholesterol
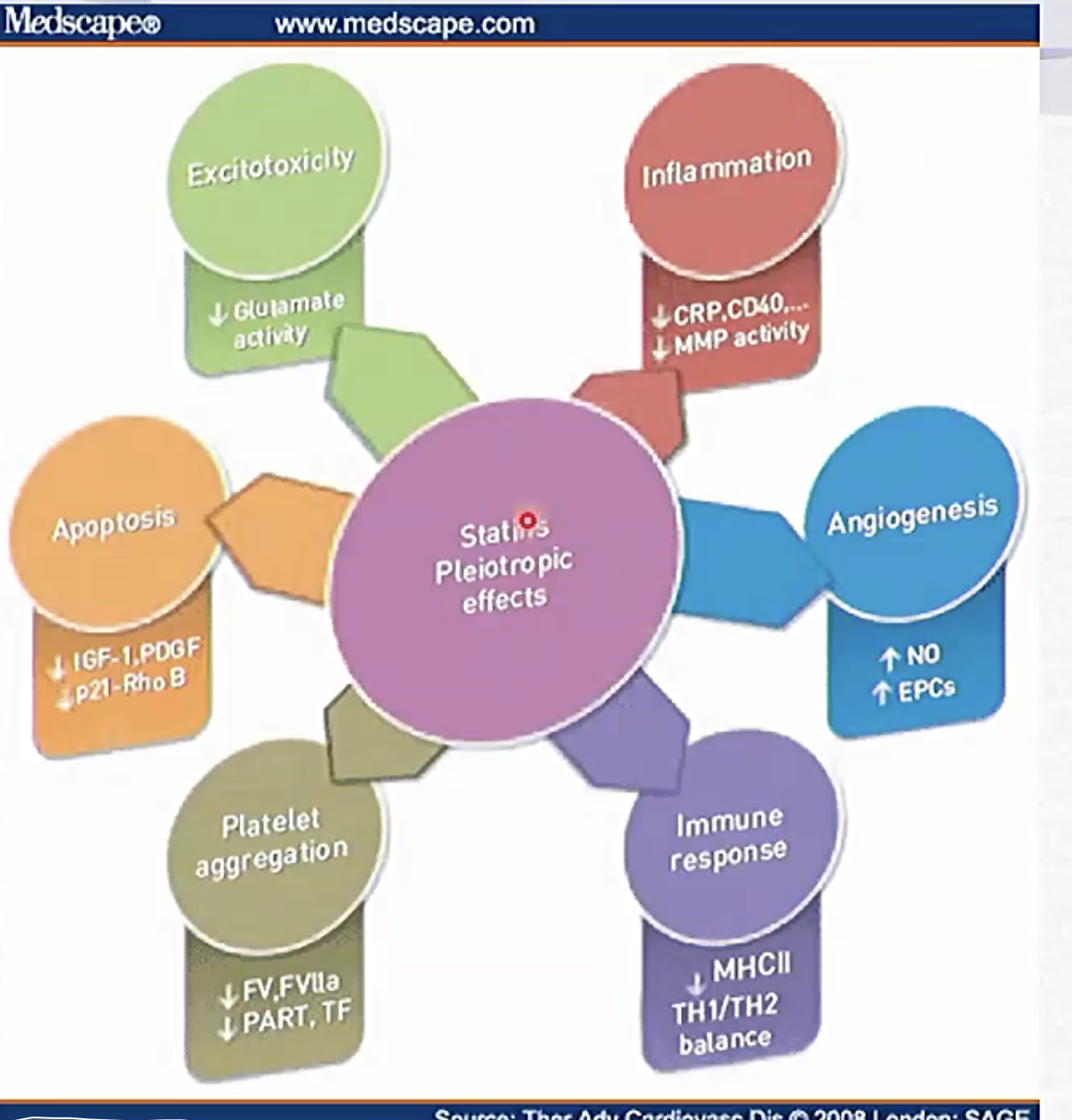
Pleiotropic effects of statins
- Lowered hepatocyte cholesterol leads to more LDL receptors being made
- anti-inflammatory
- proangiogenic
- increase immune response
- reduced platelet aggregation
- vasodilatory
Statins: major adverse reactions
- myopathy and rhabdomyolysis
- intense spreading myalgia fatigue leading to myoglobinuria renal failure and death
- dependant of plasma conc of statins statins may elevate hepatic enzymes which are markers of liver injury AVOID in pregnancy
Atorvastatin
Cholesterol uptake inhibitors
ezetimibe
stops uptake of plant sterols and cholesterol dietarily and bilary at enterocyte brush border
PCSK9 Inhibitors
binds to PCSK9
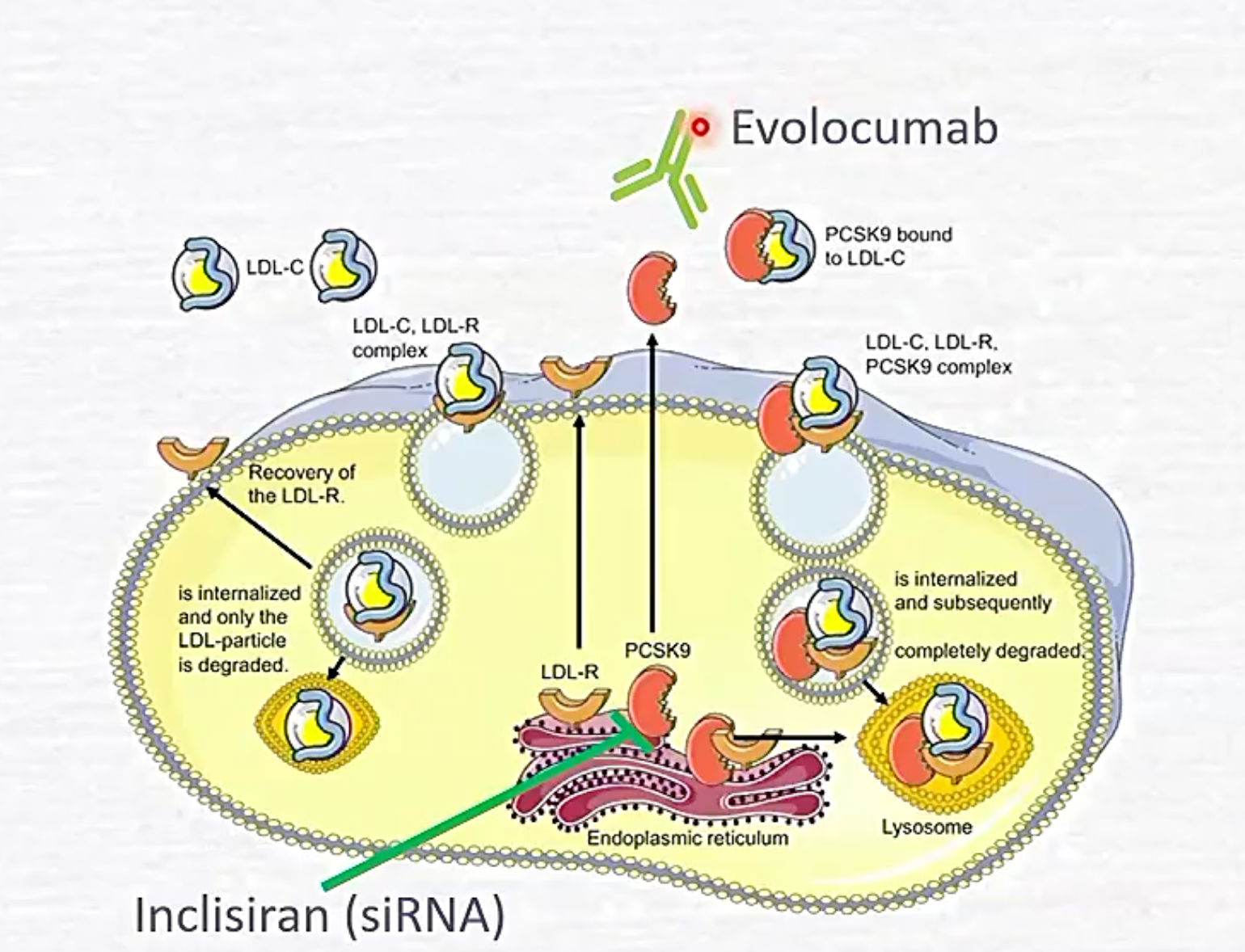
Alirocumab
for patients maxed out on statins promote LDL receptors on hepatocytes??
evolocumab
in a syringe like insulin
Inclisiran
BIle acid sequestrants
cholestyramine colestipol
Just bind to everything in the gut