Characteristics:
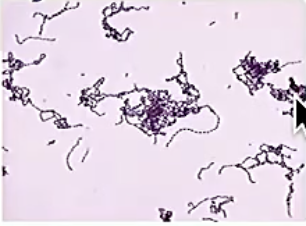
*Bacteria Form: facultative anaerobic gram-positive cocci Family:
Virulence mechanisms:
Enormous range (These lists are not exhaustive) You do not need to memorise these only appreciate the breadth of the virulence factors. Not all aureus have these all but they are present in the wider species.
- Enzymes (Invasins) (break down tissue to help spread)
- c5a peptidase
- Streptokinase
- Haemolysins (Streptolysins)
- Hyaluronidase
- DNase
- Toxins
- superantigens
- Immune evasion
- M protein
- Capsule (hyaluronic acid)
- Protein G
- Biofilms
- Surface adhesion molecules
- Teichoic acids
- F protein
- M protein
Resistances:
Infection
Areas colonised in the body (Microbiomes):
5-15% of people carry it in their pharynx. Disease associated upon new strain introduced
Infectious changes in organism:
Hospital acquired illnesses?
Clinical
Associated illnesses:
pyogenic skin and soft tissue infections (can coinfect with staphylococcus aureus)
Some important infections are:
- pharyngitis (ESPECIALLY as it related to Rheumatic fever & Rheumatic heart disease)
- Skin infections
- Pneumonia
- Endocarditis
- puerperal fever (postpartum)
- and sepsis
Post-infection can lead to:
- Rheumatic fever, acute glomerulonephritis
Testing and identifications:
Performs ß-haemolysis when cultured on blood agar Catalyse negative
This bacteria forms chains on gram-staining
Treatment and therapy:
Comments:
Generally causes more spreading infections compared to Staphylococcus Aureus